|
GMT和Pygmt提供了一个远程数据功能,可以使用函数datasets远程下载多种在线数据,并进行处理和绘图。这里以pygmt为例绘制海底地壳年龄、陆地地形。 地壳数据[1]包含了不同的分辨率,对应不同文件大小,最粗为1d,全球数据仅125K,最大分辨率1m,全球数据188M。绘图
: R4 I& H# d; X& s" b[C] 纯文本查看 复制代码 import pygmt
grid_globe = pygmt.datasets.load_earth_age(resolution='06m', region="-180/180/-90/90", registration=None)
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdimage(grid=grid_globe, projection="R15c", region="0/360/-89/89", frame=True,cmap="crustal_age.cpt")
fig.colorbar(frame=["af", "x+lage", "y+lMyr"],cmap="crustal_age.cpt")
fig.show()
5 | p4 W" i B8 I' H) X, j8 |9 w7 [2 g) p
上面的调色板crustal_age可以在.gmt/cache/下找到,而远程数据也下载到了./gmt/server/下面。 {2 g4 {/ X& i$ P: o8 P" d3 f ?7 v9 j
地形数据地形数据[2]包含多种不同分辨率,对应不同的文件大小,最粗为1d,文件大小128k,最高分辨率为1s,文件大小达41G: SRTM绘图[C] 纯文本查看 复制代码 # 雅鲁藏布江大峡谷[/b]grid = pygmt.datasets.load_earth_relief(
"03s",
region=[94, 95.5, 29, 30],
registration="gridline",
use_srtm=True,
)
# calculate the reflection of a light source projecting from west to east
# (azimuth of 270 degrees) and at a latitude of 30 degrees from the horizon
dgrid = pygmt.grdgradient(grid=grid, radiance=[270, 30])
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdimage(grid=grid, projection="M15c", region=[94, 95.5, 29, 30], frame=['WSrt+t"Original Data Elevation Model"',"xa", "ya"],cmap="dem1")
fig.colorbar(position="JML+o1.8c/0c+w10c/0.9c",frame=["af", "y+lmeter"])
fig.coast(rivers="a/1p",borders="2/5,red")
# Shift plot origin of the second map by 12.5 cm in x direction
fig.shift_origin(xshift="20c")
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="gray", series=[-1.5, 0.3, 0.01])
fig.grdimage(
grid=dgrid,
projection="M15c",
frame=['lSEt+t"Hillshade Map"', "xa0.1", "ya0.1"],
cmap=True,
)
fig.coast(rivers="a/1p",borders="2/5,red")
# Shift plot origin of the second map by 12.5 cm in x direction
fig.shift_origin(xshift="20c")
fig.grdimage(
grid=grid,
shading=dgrid,
projection="M15c",
frame=['lSEt+t"Hillshade Map"', "xa0.1", "ya0.1"],
cmap="dem1",
)
fig.coast(rivers="a/1p",borders="2/5,red")
fig.show(width="20c")
fig.savefig("srtm.png")
" W0 S8 K1 b4 Z, s
1 I2 b% b% `# q" k! m
@5 C" g' J' Z! O8 q! U* T. F+ q3D地形图. y s4 u# `, P4 |9 f
[C] 纯文本查看 复制代码 fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdview(
grid=grid,
region=[94.7, 95.2, 29.5, 30],
perspective=[250, 60],
frame=["xa", "ya", "WSNE"],
projection="M15c",
zsize="15c",
surftype="s",
cmap="dem1",
# Set the plane elevation to 1,000 meters and make the fill "gray"
plane="000+ggray",
)
fig.show()
6 H5 I8 n: W7 w L- ~+ }+ s# _8 e K; C3 C' U" o9 e
同样,我们还可以使用pygmt.grdview绘制三维地形图。下面是我曾经到过山脚下,但是在云中的南迦巴瓦峰。 . W0 @" L" X& Q% }- Z
4 y p0 ]7 i. p5 j9 T2 p1 w* ~, s* u3 \
( a7 X6 H: k1 j8 ^& \0 F2 ]
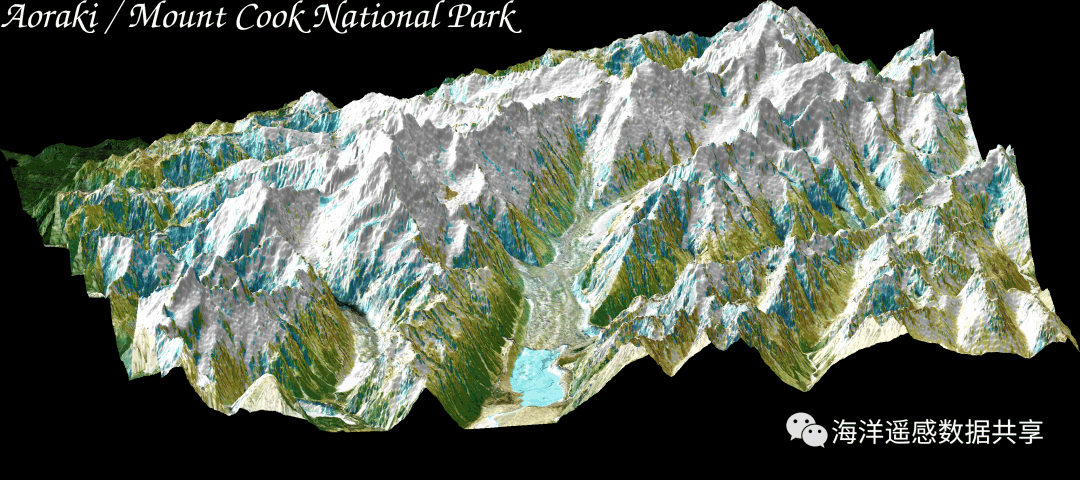
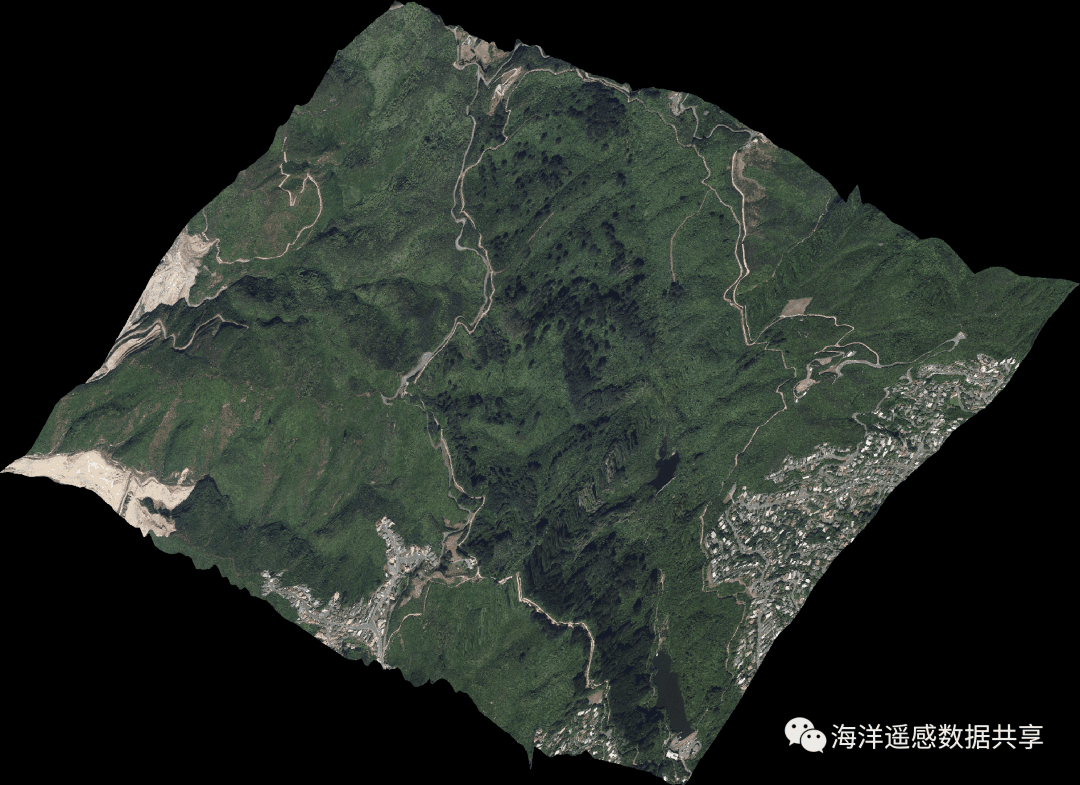
5 s3 p. b1 g9 f8 h: e! ~附:遥感影像和地形的结合在github存在一个30Day*****的系列代码库,其中包含绘图领域的30DayMapChallenge2021,恰好已经使用GMT完成了这项工作,作者是Pygmt的核心开发者Weiji。 这里有两个遥感影像和地形结合的例子(17和18),可以作为很好的学习材料.
$ V; N" D4 ^9 }: a' Y5 ~
 2 ]4 h# e: R5 ~2 k/ f
2 ]4 h# e: R5 ~2 k/ f
, M w& p+ z; I: RReferences[1] 地壳数据: https://www.generic-mapping-tools.org/remote-datasets/earth-age.html
$ \8 c" G2 v9 u2 h; p[2] 地形数据: https://www.generic-mapping-tools.org/remote-datasets/earth-relief.html
2 ]) I+ K' k& T; }7 }6 n$ O# W( n8 ^# f" y
来源:海洋遥感数据共享5 R5 b: l/ W1 N
O# p8 `: t" i/ ~7 a
|